Percussion
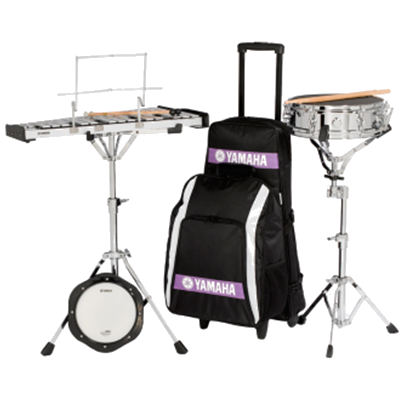
The snare drum or side drum is a percussion instrument that produces a sharp staccato sound when the head is struck with a drum stick, due to the use of a series of stiff wires held under tension against the lower skin. Snare drums are often used in orchestras, concert bands, marching bands, parades, drumlines, drum corps, and more. It is one of the central pieces in a drum set, a group of several drums, and cymbals that one player uses.